Revit Guides
Data Management
ELI5
ELI5-S2: BIM in Practice E5: Lead Appointing Party context of information exchange
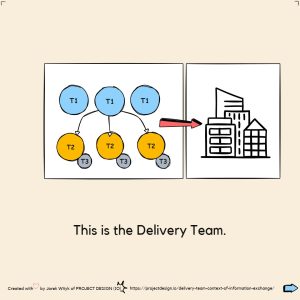
Understanding the Lead Appointed Party (T1) Context of Information Exchange in BIM
Welcome to the fifth installment of our ELI5-S2 BIM in Practice series, where we break down complex BIM concepts into easy-to-understand formats.
In this post, we will explore the context of information exchange from the perspective of the Lead Appointed Party (T1).
To help you understand the information exchange through the lens of the Lead Appointed Party and the key responsibilities, we’ve created a storyboard that visually represents these concepts.
You can view the storyboard in the carousel at the top of this page. Here, we’ll delve deeper into each point.
Key Responsibilities of the Lead Appointed Party (T1)
Security and Legal Issues
One of the primary concerns for the Lead Appointed Party is ensuring that all information exchanges comply with security protocols and legal requirements. This helps protect sensitive data and maintain project integrity.
BIM Execution Plan (BEP)
The post-appointment BIM Execution Plan (BEP) should be aligned with the Exchange Information Requirements (EIR). This alignment ensures that all project stakeholders have a clear understanding of their responsibilities and the project’s information requirements.
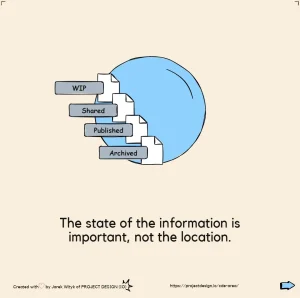
Accurate Information
The Lead Appointed Party must ensure that the information provided is accurate and properly evaluated. This involves conducting gateway checks and other validation methods to maintain data integrity.
Project Delivery Focus
The Lead Appointed Party often focuses on the documentation required for the project delivery phase. Ensuring that this documentation is comprehensive and accurate is critical for the smooth execution of the project.
Client Perspective
Viewing deliverables through the client’s eyes can provide valuable insights. This approach helps ensure that the project’s outcomes align with the client’s expectations and needs.
Methods and Processes
There are often challenges related to the methods and processes for acquiring information. The Lead Appointed Party is responsible for managing these processes to ensure efficiency and accuracy in data collection.
Responsibility Transfer
Handling the transfer of responsibility between different project phases and stakeholders is another key duty of Lead Appointed Party. This ensures that all parties are aware of their roles and responsibilities at each stage of the project.
Training Management
The Appointed Party must manage the training of their team, including the supply chain and often the Facility Maintenance team. Proper training ensures that all team members are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to fulfill their roles effectively.
Conclusion
By understanding the project through the Lead Appointed Party lens, we can better manage the challenges faced in BIM projects. This perspective is crucial for improving the efficiency and success of information management in construction projects.
We hope this storyboard and blog post have provided you with a clearer understanding of the T1 role in BIM. For more insights and updates, stay tuned to our blog and continue exploring our ELI5-S2 BIM in Practice series.