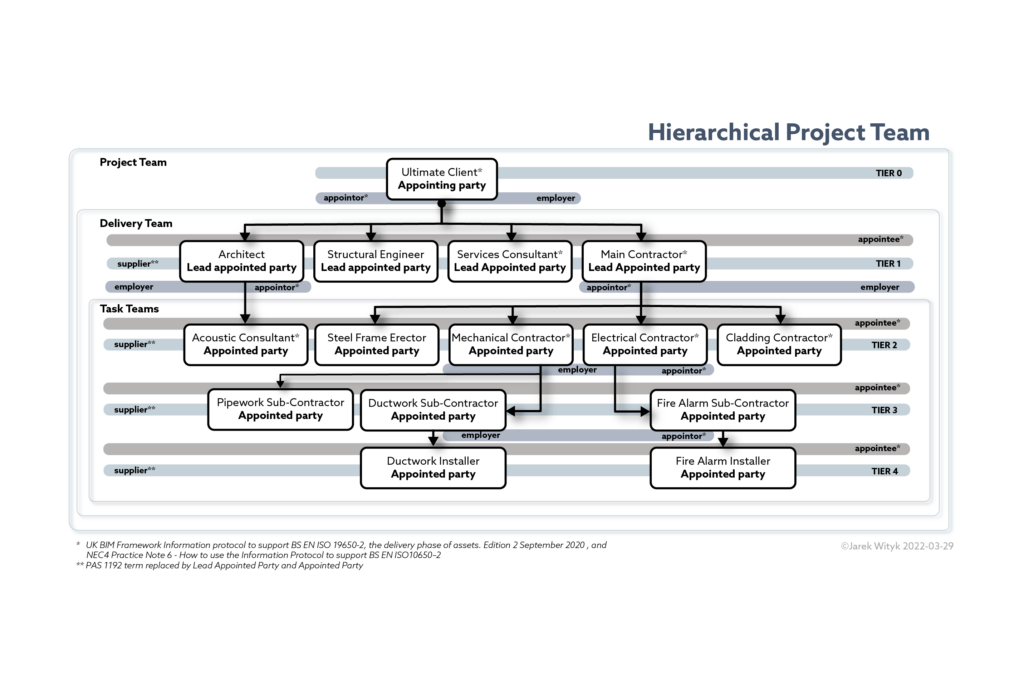
The transition from the BIM Levels to the concepts in the ISO 19650 series and the UK BIM Framework represents a shift in how we think about BIM maturity. However, for those accustomed to the BIM Levels, understanding how these levels correspond to the new framework can be helpful. Here’s a comparison to provide some context:
BIM Levels (Previous Approach)
- Level 0 – No Collaboration: Utilization of 2D CAD, with data typically shared in paper or electronic paper formats. No collaboration tools or processes are in place.
- Level 1 – Managed CAD in 2D or 3D: Use of 3D CAD for conceptual work and 2D for statutory approval documentation. Data is shared electronically, but there’s a lack of collaborative working and integration between disciplines.
- Level 2 – Managed 3D Environment with Data Structuring: Collaboration among different parties, each using their own 3D CAD models. Data is shared in a common file format. The use of a Common Data Environment (CDE) is introduced for information sharing.
- Level 3 – Full Collaboration: Integration and collaborative working with a single, shared project model stored in a centralized repository. This level is aspirational and represents a fully integrated and collaborative process across all disciplines.
ISO 19650 / UK BIM Framework (Current Approach)
- Organizational Information Requirements (OIR): Strategy-level requirements by an organization to achieve its goals through information.
- Asset Information Requirements (AIR): The information needed related to assets for operational, maintenance, or disposal purposes.
- Project Information Requirements (PIR): Specific information needs for a project, forming the basis for the Employer’s Information Requirements (EIR).
- Employer’s Information Requirements (EIR): The information deliverables required by the employer, including formats and standards.
- BIM Execution Plan (BEP): A document outlining how the information modelling aspects of a project will be carried out.
- Common Data Environment (CDE): A shared online space for managing and storing project information.
- Information Delivery Cycle: Process for managing and delivering information throughout the lifecycle of an asset.
Comparison and Transition
The ISO 19650 series and UK BIM Framework don’t directly translate to the old BIM Levels but rather offer a more comprehensive and flexible approach. Where BIM Levels were more about the technology and processes for creating and managing digital models, the ISO 19650 series focuses on the broader spectrum of information management across an asset’s lifecycle.
In essence, the ISO 19650 and UK BIM Framework encapsulate the principles and practices of BIM Level 2 and expand upon them, focusing more on the management, standardization, and integration of information across the lifecycle of a built asset rather than simply the level of model detail or collaboration technology used. The transition represents a move from a technology-centric view of BIM to a more holistic information management approach, considering the entire lifecycle of built assets.