jet
Revit Guides
Data Management
extinguishing medium, usually water, leaving a nozzle as a continuous stream, water spray, or water
BS 4422 2005
fog (mist)
- Continuous Stream: When water is expelled as a continuous stream, it means the water flows in a steady, unbroken line from the nozzle. This method is effective for delivering a large amount of water to a specific point, making it useful for deeply-seated fires or for reaching long distances.
- Water Spray: In this mode, the water is dispersed in a spray pattern. This creates a wider area of coverage compared to a continuous stream. Water sprays are effective for covering larger surface areas and can be used to cool down surrounding areas to prevent the spread of fire.
- Water Fog (Mist): When water is expelled as a fine mist, it creates a fog-like effect. This method is especially effective for absorbing heat and reducing temperatures rapidly. The fine droplets of water in the mist have a larger surface area in contact with the fire, which helps in quicker heat absorption and also in creating a barrier that limits the access of oxygen to the fire.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and is chosen based on the nature of the fire, the environment, and the specific goals of the firefighting effort (such as direct extinguishing, creating firebreaks, or cooling). The design of the nozzle and the pressure of the water are key factors in determining the pattern of the jet.
2022-07-11
No Comments
Blog
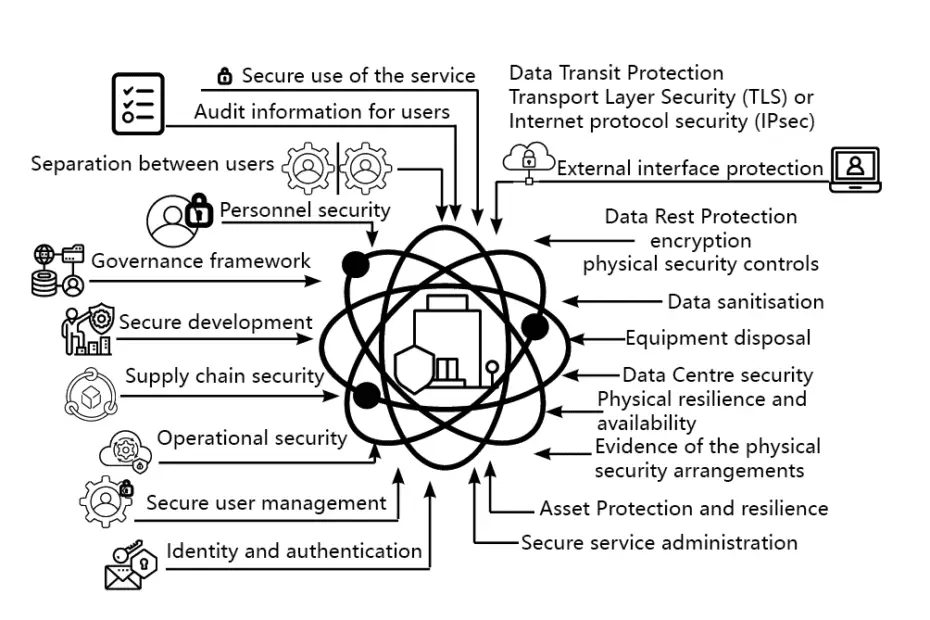
Management of the cyber-security threats in Common Data Environment
The increased reliance of the IT Technology Widely used cloud-based
2020-07-25
No Comments
Management of duplicates
The procedure to remove duplicate properties shall be carried out
2022-07-24
No Comments

