Revit Guides
Data Management
ELI5
Electrical & Mechanical Equipment: Access & Maintenance (UK)
“All controlgear shall be mounted so as to facilitate its operation and maintenance. Where a special tool is necessary to adjust, maintain, or remove a device, such a tool shall be supplied. Where access is required for regular maintenance or adjustment, the relevant devices shall be located between 0,4 m and 2,0 m above the servicing level. It is recommended that terminals be at least 0,2 m above the servicing level and be so placed that conductors and cables can be easily connected to them.” BS EN 60204-1:2018+A1:2025
TL;DR
There is no universal “1 m rule” in UK law or BS 7671. The legal duty is to provide adequate working space, access and lighting (EAWR Reg. 15). Legislation.gov.uk
Numbers appear when you’re in restricted-access electrical rooms (BS 7671 Section 729: operating/maintenance gangways) and from manufacturer instructions. electrical.theiet.org+1
Some sectors/clients (e.g., UK water industry via WIMES) do require ~1 m clearance — that’s client/sector spec, not law. pumpcentre.com+1
1. What the law actually requires (baseline for every project)
EAWR Reg. 15: provide adequate working space, adequate means of access and adequate lighting at electrical equipment where work may give rise to danger. This is your non-negotiable legal anchor for layouts and clearances. Legislation.gov.uk
CDM 2015 (designer duty): design to eliminate, reduce or control foreseeable risks; provide enough information with the design so others can comply. (Use this to justify room sizing, door swing, heavy-item removal routes, etc.) Legislation.gov.ukHSE
HSG85: practical HSE guidance on safe working around electrical gear (planning, safe access/space, lighting). Use it to evidence your maintenance reasoning alongside EAWR. HSEhealthandsafety-services.co.uk
Fire service access overlay (ADB B5): coordinate plant room locations and external access with the vehicle access rules (e.g., a door every ≤ 60 m on accessible elevations; min 750 mm door width). GOV.UK
- Wiring inside enclosures: It is recommended that electrical equipment mounted inside enclosures be designed and constructed in such a way as to permit modification of the wiring from the front of the enclosure. Where that is not practicable and control devices are connected from the rear of the enclosure, access dors or swingout panels shall be provided. BS EN 60204-1:2018+A1:2025
2. When BS 7671 gives you actual numbers
In restricted-access electrical rooms (e.g., switchrooms, locked plant areas/roofs reserved for skilled/instructed persons), BS 7671 Section 729 sets minimum gangway/working-space envelopes and related conditions for operation and maintenance. Typical design outcomes include:
Baseline gangway (barriers/enclosures as basic protection)
– Working width around ≥ 700 mm
– Headroom around ≥ 2000 mm
– Keep live parts out of normal reach (often taken as ≥ 2500 mm).Encroachment while doors are open / withdrawable gear
– Preserve a passing width during maintenance, keep safe door swing (≥ 90°) and working depth at fronts.Long line-ups, exits & doors
– Long gangways should be accessible from both ends (triggered around 10–20 m depending on room geometry and dooring); doors/hinged panels to open ≥ 90°.
These are BS 7671 figures/conditions specific to restricted areas. Always check the current edition (and any manufacturer overlay). electrical.theiet.org+1
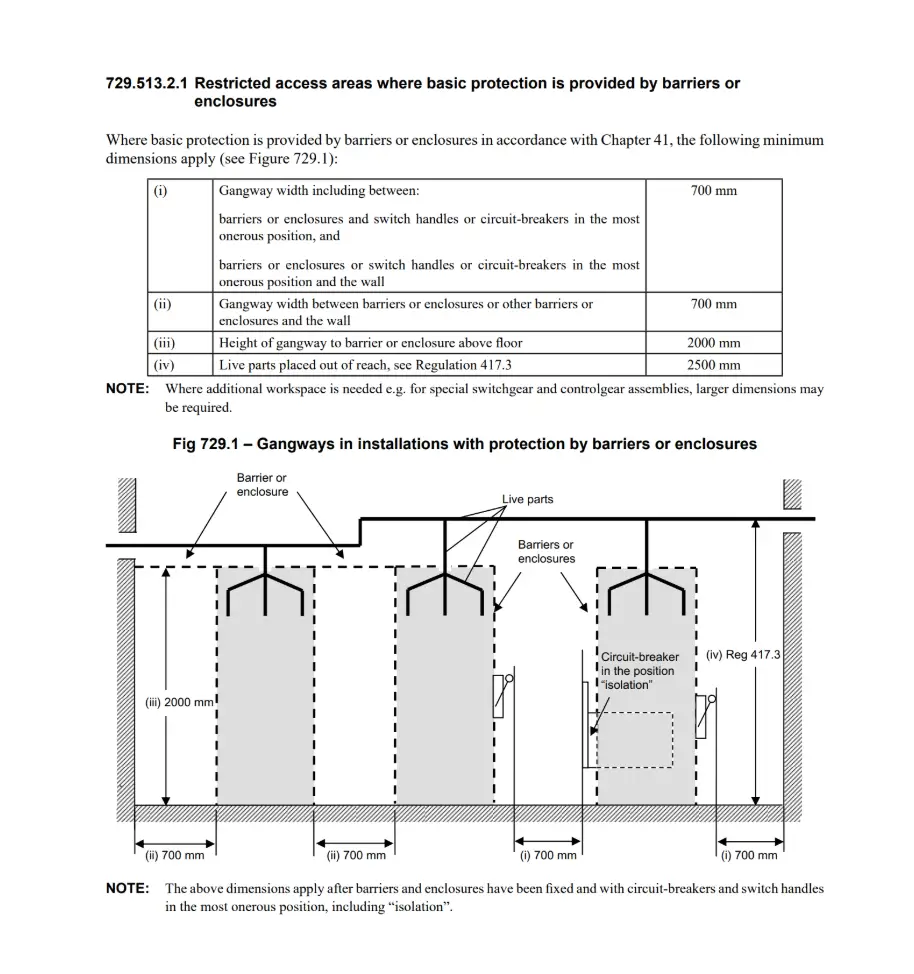
If protective measure is barriers/enclosures → 700 mm / 2000 mm / 2500 mm.
If unprotected live parts (one side) → 900 mm gangway; 700 mm in front of controls; 2500 mm to live parts.
If live parts on both sides → 1300 mm between live parts; 1100 mm min from handle to opposite live parts; 900 mm free in front of controls; 2500 mm to live parts. Iteh Standards
Restricted vs. open‑access context (who the room is for)
Restricted access areas must be signed and kept locked to skilled or instructed persons only; unauthorised persons must not have access. (This is the premise for applying Section 729 numbers to panel/DB rooms.) Iteh Standards
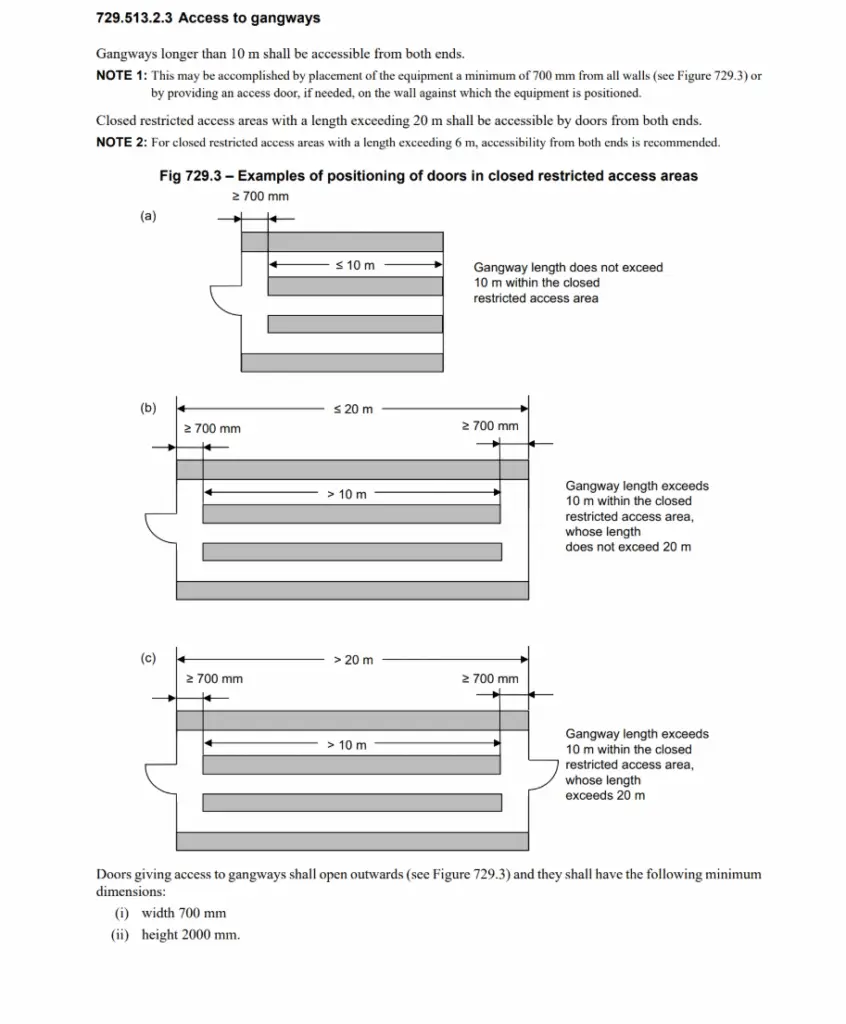
End wall clearance for long runs
For long line‑ups, place equipment a minimum of 700 mm from end walls (or provide a second door) so gangways > 10 m are accessible from both ends. Closed restricted‑access areas > 20 m must have doors at both ends. Iteh Standards
Isolation & emergency switching (applies to all panels/DBs)
Ensure suitable means are available for cutting off the supply and for isolation; “isolation” means secure disconnection and separation from every source of electrical energy. (Position, labelling and access to these devices must reflect the EAWR duty.) Legislation.gov.uk
Consumer units / DBs in general spaces: Where boards are not in restricted rooms (e.g., riser cupboards serving common parts), lean on EAWR 15 + manufacturer’s instructions for safe working space and isolation reach; avoid inventing numeric “working depth” unless the OEM specifies one. Legislation.gov.ukIET Electrical
However, in dwellings, advice on mounting height for equipment not intended for regular user interaction (like meter cupboards, consumer units or router, etc.)
“Reasonable provision should be made to ensure that the approach route to any communal facilities that serve the dwelling meets these provisions. Communal facilities include storage areas, such as those used for depositing refuse and recycling, but not plant rooms or other service areas unless occupants need regular access, for example for meter reading.” ADM Section 2A Clause 2.4
“Consumer units are mounted so that the switches are 1350-1450mm above floor level” ADM Clause 1.18
3. Access during maintenance (doors/withdrawable gear)
Maintain a minimum passing width of 700 mm in use. Where doors can be fixed open or circuit-breakers are fully withdrawn, keep ≥ 500 mm to the opposite limitation.
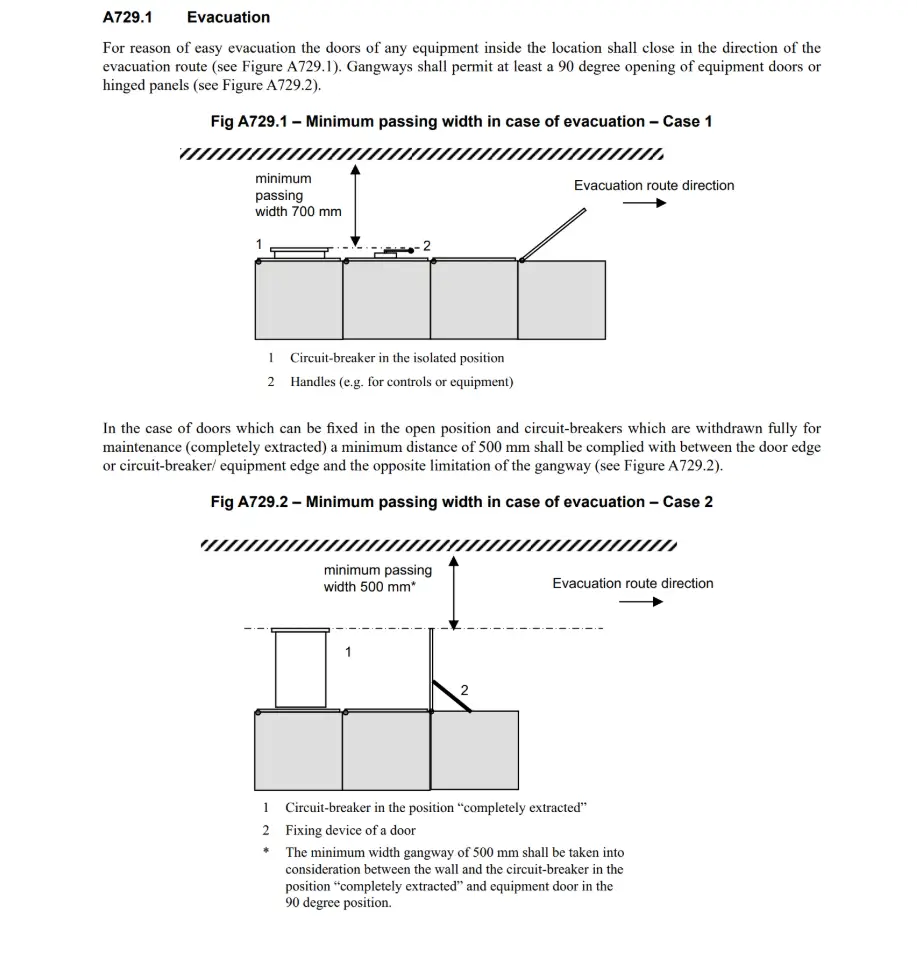
4. Length, exits and door geometry
Gangways > 10 m shall be accessible from both ends; closed restricted‑access areas > 20 m shall be accessible by doors from both ends. Doors/hinged panels shall open to ≥ 90°.”
“Doors giving access to closed restricted areas must allow evacuation to the outside without the use of a key or tool, and gangways must allow equipment doors/panels to open to ≥ 90°. (Outward opening is strongly recommended and often adopted to facilitate evacuation.)”
5. Where “1 m clearance” comes from
credit: Dan Oxford
The Water Industry Mechanical and Electrical Specifications WIMES 3.02 Low Voltage Electrical Installations extends the BS7671 access requirement to 1000mm
“The minimum distance specified for the width of a maintenance gangway in Section 729 of BS 7671 is 700 mm, however, extending this to 1000 mm in this Specification is considered a reasonable measure to facilitate all foreseeable Assembly installation, operation and maintenance activities.” WIMES 3.02 – Low Voltage Electrical Installations Clause 3.3.5
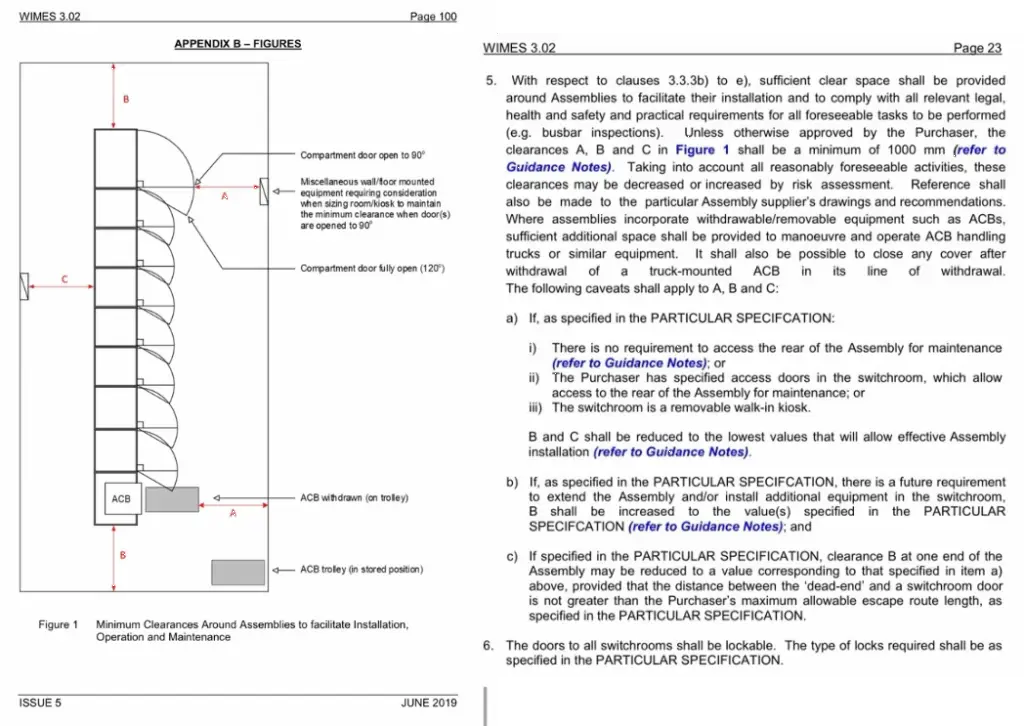
Manufacturer’s instructions
The selection/erection must take account of manufacturer’s instructions. If an OEM or specification calls for ≥ 1000 mm frontal working depth, that becomes the project requirement over and above the 700 mm minimum, for example : https://www.se.com/uk/en/faqs/FA32222/
6. Firefighting access (layout coordination)
Provide reasonable facilities to assist fire-fighters and reasonable provision within the site for fire appliance access. Use this to coordinate plant-room locations, switchgear access routes and external yard clearances with ADB B5. GOV.UK
For small buildings: provide access to the lesser of 15% of perimeter or within 45 m of every footprint point.
Each accessible elevation to have doors at ≤ 60 m spacing (min 750 mm wide).
clause 15.3. GOV.UK
7. Practical layout rules
Step 1 — Classify the space
Restricted-access electrical rooms/areas (switchrooms, risers, plant decks; skilled/instructed persons only): apply BS 7671 Section 729 for operating/maintenance gangways and working space (plus OEM instructions).
General access areas: default to EAWR Reg. 15 (adequate working space, access and lighting) and HSG85 safe-working guidance. Legislation.gov.ukHSE
Step 2 — Overlay Part M correctly
Dwellings (Volume 1): where Part M applies, keep wall-mounted switches/sockets within 450–1200 mm A.F.L., and mount consumer unit switches 1350–1450 mm A.F.L. (Diagram 1.5). GOV.UK
Buildings other than dwellings (Volume 2): apply the accessibility objectives in user-facing spaces. But: Requirement M1 does not apply to any part of a building used solely to enable the building or any service or fitting to be inspected, repaired or maintained — i.e., plant rooms/risers aren’t Part M spaces. Use EAWR/HSG85 + BS 7671/OEM there. GOV.UK
Step 3 — Overlay manufacturer & client/sector specs
If the OEM asks for >700 mm or a specific service envelope (e.g., to withdraw ACBs), use that (BS 7671 510.3 principle).
If the client/sector has a standard (e.g., WIMES in the water industry specifying ~1 m around LV assemblies), adopt it as a project requirement.
Step 4 — Egress & doors during maintenance
Maintain safe egress while panels/doors are open. Keep a usable passing width with doors/panels at ≥90° and plan working space so operatives aren’t forced into live zones. (Use your BS 7671 Section 729 logic for restricted rooms and OEM service envelopes for each assembly.)
Two-way access for long line-ups. Where gangways are long or end-blocked by withdrawable gear, provide access from both ends (apply your Section 729 criteria).
Fire service access (ADB overlay). Where relevant to the plant location, check external door spacing/widths to support FRS access/egress.
If your client/sector adopts WIMES 3.02 (water industry): treat ~1 m clearance around LV assemblies as a hard constraint to allow:
full door opening and safe operator stance,
withdrawal of ACBs/draw-out units for routine maintenance,
a clear emergency escape route in front of the assembly.
Show the 1 m envelope on GAs/elevations, keep it free of other services/cable ladders, and reference it in your room data sheet/spec. (WIMES is a client/sector specification, not legislation—apply where the project requires it; thanks to Dan Oxford for flagging this nuance.)
Step 5 — Record the rationale (CDM)
In the design risk register/spec: state the room classification, the rule-set applied (EAWR/HSG85/BS 7671/Part M/OEM/WIMES), how evacuation is maintained during maintenance, and show removal routes for heavy components.
8. Means of escape for fire safety
Part B of the Building Regulations (England) sets fire safety requirements for building work.
Approved Document B gives guidance:
Volume 1 — dwellings
Volume 2 — non-dwellings
Tables 8–10 apply to non-dwellings.
Other approaches may be valid—check with the project’s fire safety consultant and building control body.
Minimum widths of escape routes and exits
| Maximum number of people | Minimum width |
|---|---|
| 60 | 750 mm |
| 110 | 850 mm |
| 220 | 1,050 mm |
| More than 220 | 5 mm per person |
Minimum number of escape routes and exits from a room, tier or storey
| Minimum number of people | Minimum number of escape routes |
|---|---|
| 60 | 1 |
| 600 | 2 |
| more than 600 | 3 |
Maximum travel distance for escape
| Type of building | Maximum travel distance for escape available in one direction | Maximum travel distance for escape available in at least two directions |
|---|---|---|
| Residential (institutional) | 9 m | 18 m |
| Residential (other) in bedrooms [i] | 9 m | 18 m |
| Residential (other) in bedroom corridors [ii] | 9 m | 35 m |
| Residential (other) elsewhere | 18 m | 35 m |
| Offices | 18 m | 45 m |
| Shop and commercial premises | 18 m | 45 m |
| Assembly and recreation buildings primarily for disabled people | 9 m | 18 m |
| Assembly and recreation buildings with fixed seating in rows | 15 m | 32 m |
| Assembly and recreation buildings (elsewhere) | 18 m | 45 m |
| Industrial buildings, storage and other non-residential (normal hazard) [iii] | 25 m | 45 m |
| Industrial buildings, storage and other non-residential (higher hazard) [iii] | 12 m | 25 m |
| Place of special fire hazard [iv] | 9 m [v] | 18 m [v] |
| Plant room or rooftop plant (distance within the room) | 9 m | 35 m |
| Plant room or rooftop plant with escape route not in open air (overall travel distance) | 18 m | 45 m |
| Plant room or rooftop plant with escape route not in open air (overall travel distance) | 60 m | 100 m |
Notes:
[i] Maximum part of travel distance within the room. This limit applies within the bedroom and any associated dressing room, bathroom or sitting room, etc. The distance is measured to the door to the protected corridor that serves the room or suite.
[ii] Maximum part of travel distance applying from that point along the bedroom corridor to a storey exit.
[iii] The appropriate travel distance depends on the level of fire hazard associated with the processes and materials being used. For the definition of higher hazard, refer to Approved Document B Volume 2[7].
[iv] This is defined as a room such as an oil-filled transformer room, switch gear room, boiler room, storage space for fuel or other highly flammable substances or a room that houses a fixed internal combustion engine.
[v] Maximum part of travel distance within the room/area. Travel distance outside the room/area should comply with the limits for the purpose group of the building or part.
General note:
If the internal layout of partitions, fittings, etc. is not known, direct distances, rather than travel distances, should be assessed. The direct distance should be assumed to be two-thirds of the actual travel distance.
9. Human factors & reach distances
Maintenance reach levels: Maximum 2100mm above floor level
Passageway:
– Height: 2100 mm minimum
– Passageway width: 550 mm minimum – 750mm optimum
Working positions:
– Standing work: 900 mm – 1.5m working height optimum
– Kneeling: 600 mm – 1.2 m working height
Access routes:
– Passageways: 550 mm minimum, 750 mm optimum
– Stairs: 600 mm to 750mm one person, 1.1 m minimum, two people.
Source: BS 8313 as amended in BSRIA BG 55
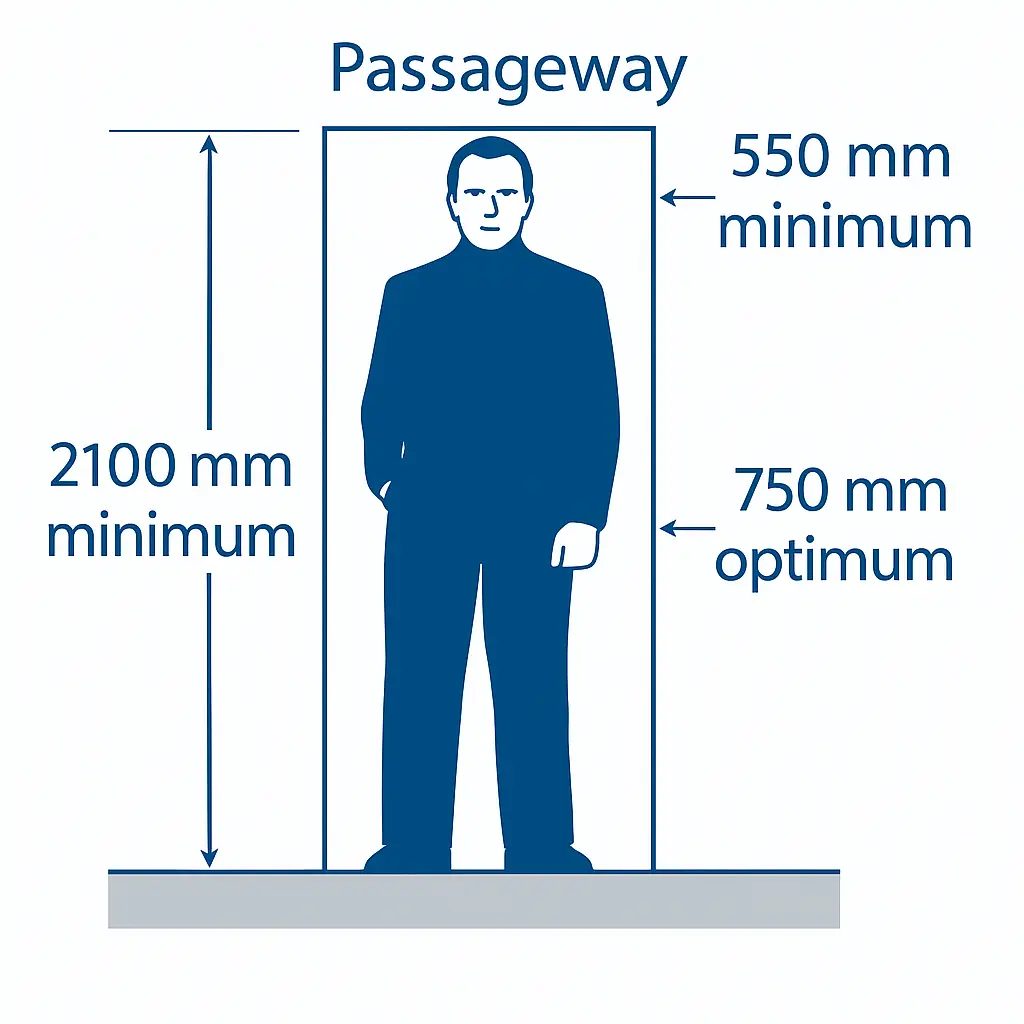
Image Source: Based on BS 8313 and amended in BG 55
10. BG 84_2024 Space planning allowances (early design stage)
During concept design and feasibility studies, use industry-standard space and weight allowances to size plant rooms, coordinate structural loads, and verify access routes before detailed equipment selection. These rule-of-thumb allowances from BSRIA BG 84/2024 provide approximate space envelopes for common building services equipment, including maintenance access, concrete bases, cable/pipe clearances, and heat dissipation zones.
Key applications:
– Plant room sizing during architectural coordination
– Structural loading estimates for slab design
– Access route planning for equipment delivery and replacement
– Space budgeting across mechanical and electrical disciplines
Important: These are preliminary allowances only. Always verify with manufacturer datasheets, detailed calculations, and current standards during detailed design stages. The responsibility for safe and appropriate application rests with qualified professionals.
The following table consolidates key clearance requirements from construction industry data and British Standards:
| Category | Equipment | Clearance_Type | Dimension | Location | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment Installation | Biomass Boilers | Base allowance | 150 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 1 - Biomass boiler plant room area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Air Cooled Condensers | Base and anti-vibration mounts | 300 mm | Below | Base and anti-vibration mounts allowance | Figure 4 - Air cooled condensers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Air Cooled Condensers | Heat dissipation clearance | Clear height required | Above | Clear height above units must be provided for vertical air discharge to allow heat to dissipate | Figure 4 - Air cooled condensers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Air Handling Units | Base and condensate trap | 200 mm | Below | Base and condensate trap allowance | Figure 6 - Air handling units area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Air Handling Units | Crawl space above unit | 790 mm | Above | Crawl space above each unit for maintenance access | Figure 6 - Air handling units area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Gas Fired Boilers | Base allowance | 150 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 8 - Gas fired boiler plant room area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Horizontal Calorifiers | Base allowance | 100 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 10 - Horizontal calorifiers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Horizontal Calorifiers | Pipework clearance | 1,000 mm | Above | Height allowance for pipework | Figure 10 - Horizontal calorifiers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Vertical Calorifiers | Base allowance | 100 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 12 - Vertical calorifiers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Vertical Calorifiers | Pipework clearance | 1,000 mm | Above | Height allowance for pipework | Figure 12 - Vertical calorifiers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Air Cooled Chillers | Base and anti-vibration mounts | 300 mm | Below | Base and anti-vibration mounts allowance | Figure 14 - Air cooled chillers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Air Cooled Chillers | Heat dissipation clearance | Clear height required | Above | Clear height above units must be provided for vertical air discharge to allow heat to dissipate | Figure 14 - Air cooled chillers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Water Cooled Chillers | Base and anti-vibration mounts | 300 mm | Below | Concrete base and anti-vibration mounts allowance | Figure 16 - Water cooled chillers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Forced Draught Cooling Towers | Base allowance | 200 mm | Below | Base allowance for foundation | Figure 18 - Forced draught cooling tower area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Forced Draught Cooling Towers | Heat dissipation clearance | Clear height required | Above | Clear height above units for vertical air discharge to allow heat to dissipate | Figure 18 - Forced draught cooling tower area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Induced Draught Cooling Towers | Base allowance | 200 mm | Below | Base allowance for foundation | Figure 20 - Induced draught cooling tower area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Induced Draught Cooling Towers | Heat dissipation clearance | Clear height required | Above | Clear height above units for vertical air discharge to allow heat to dissipate | Figure 20 - Induced draught cooling tower area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Cold Water Storage Tanks | Base allowance | 150 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 22 - Cold water storage area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Cold Water Storage Tanks | Freeboard height | 500 mm | Above water level | Freeboard height allowance above maximum water level | Figure 22 - Cold water storage area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Cold Water Storage Tanks | Crawl space above tank | 790 mm | Above | Crawl space above tank for maintenance access | Figure 22 - Cold water storage area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Cold Water Storage Tanks (External Flange) | Additional height for external flange | 500 mm | Above | Additional height allowance if externally flanged tank is used | Figure 22 - Cold water storage area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Diesel Generators | Base and anti-vibration mounts | 300 mm | Below | Concrete base and anti-vibration mounts allowance | Figure 24 - Diesel generators area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Diesel Generators | Crawl space above unit | 790 mm | Above | Crawl space above unit for maintenance access | Figure 24 - Diesel generators area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Hybrid Rotary UPS | Base allowance | 100 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 26 - Hybrid rotary UPS area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Hybrid Rotary UPS | Cable installation height | 1,000 mm | Above | Height allowance for cable installation | Figure 26 - Hybrid rotary UPS area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Static UPS | Cable installation space | Additional space required | Top and bottom | Additional space should be provided at top and bottom for cable installation | Figure 28 - Static UPS area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Static UPS (≥400 kVA) | Cooling clearance | 400 mm | Above | Additional clearance at top for cooling purposes for UPS rated 400 kVA or above | Figure 28 - Static UPS area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Static UPS | Rear cooling space | Per manufacturer specifications | Behind | Additional space for cooling at rear in accordance with manufacturer specifications | Figure 28 - Static UPS area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Packaged Substations | Base allowance | 100 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 30 - Packaged substations area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Packaged Substations | Crawl access space | 790 mm | Above | Crawl access space above unit for maintenance | Figure 30 - Packaged substations area and height |
| Equipment Installation | UPS Battery Racks | Maximum safe height | 2,000 mm maximum | Above floor | For safe access to battery rack, height should not exceed 2 m | Figure 32 - UPS battery rooms area and height |
| Equipment Installation | LV Switch Rooms (up to 750 kVA) | Cable installation height | 1,000 mm | Above | Height allowance for cable installation for ratings up to 750 kVA | Figure 34 - Switch rooms area and height |
| Equipment Installation | LV Switch Rooms (≥1,000 kVA) | Cable installation height | 1,500 mm | Above | Height allowance for cable installation for ratings 1,000 kVA and above | Figure 34 - Switch rooms area and height |
| Equipment Installation | LV Switch Rooms | Base allowance | 100 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 34 - Switch rooms area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Transformers | Base allowance | 100 mm | Below | Concrete base allowance | Figure 36 - Transformers area and height |
| Equipment Installation | Transformers | Cable installation height | 1,000 mm | Above | Height allowance for cable installation | Figure 36 - Transformers area and height |
| Maintenance Access | Switchgear | Operating and maintenance gangways | 700 mm minimum | All sides | Gangways should permit at least 90° opening of equipment doors or hinged panels | Figure 38 - Switchgear space for operating and maintenance (Based on BS 7671) |
| Safety | Switchgear | Safety clearance from live parts | 2,000 mm height, 2,500 mm overall | Above and around live parts | For placing electrical equipment out of reach per BS 7671 Regulation 417.3 | Figure 38 - Switchgear space for operating and maintenance (Based on BS 7671) |
| Building Services | Ceiling Voids - Structural | Structural deflection | 50 mm | Above structural elements | Allowance for structural deflection plus tolerance | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Ceiling Voids - Sprinkler | Sprinkler zone | 50 mm + 150 mm | Above other services | Clearance zone for sprinkler systems | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Ceiling Voids - Lighting | Lighting zone | 150 mm | Below ceiling | Zone allocation for lighting installations | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Ceiling Voids - Luminaires | Luminaire removal clearance | 1.5 times luminaire height | Around luminaires | Clearance to facilitate removal of lighting fittings and heat dissipation | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Ceiling Voids | Ceiling deflection | 50 mm | Below ceiling | Allowance for ceiling deflection | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Floor Voids - Office | Typical office access | 150 mm minimum | Under raised floor | Minimum access space under raised floors for typical offices | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Floor Voids - Trading Floor | Trading floor access | 300-500 mm | Under raised floor | Enhanced access space for trading floors | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Access Panels | Minimum panel size | 600 mm x 600 mm minimum | Multiple locations | Minimum size for access panels throughout building services | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Building Services | Terminal Units | Maintenance access | 500 mm minimum | Around terminal units | Clear access to terminal units for maintenance | Figure 39 - Ceiling and floor voids in a generic office building |
| Maintenance Reach | Standing Maintenance Work | Maximum reach height | 2,100 mm maximum | Above floor level | Maximum height for safe standing maintenance access | Figure 40 - Space requirements and reach distances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Maintenance Reach | Prone Maintenance Work | Minimum height for prone access | 450 mm | Height clearance | Minimum height required for prone maintenance position | Figure 40 - Space requirements and reach distances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Maintenance Reach | Crawl Maintenance Work | Minimum height for crawling | 900 mm | Height clearance | Minimum height required for crawling maintenance access | Figure 40 - Space requirements and reach distances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Maintenance Reach | Stooping Maintenance Work | Minimum height for stooping | 900 mm | Height clearance | Minimum height required for stooping maintenance work | Figure 40 - Space requirements and reach distances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Maintenance Reach | Squatting Maintenance Work | Minimum height for squatting | 690 mm | Height clearance | Minimum height required for squatting maintenance position | Figure 40 - Space requirements and reach distances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Maintenance Reach | Kneeling Maintenance Work | Minimum height for kneeling | 1,100 mm | Height clearance | Minimum height required for kneeling maintenance work | Figure 40 - Space requirements and reach distances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Passageway - Single Person | Width | 550 mm minimum, 750 mm optimum | Width | Width requirement for single person passage | Figure 40 - Space requirements and reach distances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Ladder | Width | 380 mm minimum, 450 mm optimum | Width | Ladder width requirements for safe access | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Ladder | Side clearance | 600 mm minimum | Between side walls | Clear space required around ladder between side walls | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Inclined Ladder | Width with handrails | 530-600 mm | Width including handrails | Width including handrails for inclined ladders | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Stairs - Single Person | Width | 600-750 mm | Width | Width for single person stair access | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Stairs - Two Person | Width | 1,100 mm minimum | Width | Width for two people on stairs simultaneously | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Ramp | Width | 750 mm minimum, 1,100 mm optimum | Width | Ramp width requirements for safe access | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Ladder Rungs | Rung spacing and diameter | 180-406 mm spacing, 20-40 mm diameter | Vertical spacing and rung size | 300 mm optimum spacing, standard rung diameter range | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |
| Access Routes | Stair Treads and Risers | Tread and riser dimensions | 240 mm optimum tread, 250 mm maximum riser | Stair geometry | Optimum tread depth and maximum riser height for safety | Page 48 - Access route clearances (Based on BS 8313 amended in BG 55) |








3 responses
Your blog is a true hidden gem on the internet. Keep up the excellent work!
Hey Jarek, just reading your latest post about clearance rules.
Your 100% correct you won’t find a blanket 1,000 mm clearance rule written into UK legislation or BS 7671 as far as I’m aware.
Exactly as you said, Legislation / ADB / HSG85 / CDM all talk about providing safe access, safe working space, and designing out maintenance risks, but none of them give a fixed measurement.
My work is mainly in the water industry, and this is where the 1 m clearance does appear – but only in sector or client specifications, not in the regs. The water industry standard WIMES 3.02 calls for 1 m clearance around LV assemblies so you can open doors properly, withdraw ACBs for normal operation and maintenance, and provide safe escape in an emergency.
Let me know if you find anything.
Thanks,
Dan
Thanks, Dan — really appreciate you sharing the water-industry context. I’ve updated the post thanks to you.